PET Bottle Label Visual Inspection Technology: A "Sharp Eye" for Packaging Quality
On high-speed PET bottle production lines, visual inspection systems accurately identify various label defects at a rate of hundreds of bottles per minute, becoming a critical line of defense for ensuring product quality.
In industries such as food, beverages, and pharmaceuticals, PET bottles have become a mainstream packaging format due to their lightweight and unbreakable properties. As production line speeds continue to increase, manual inspection is no longer sufficient to meet the demands of modern production.
Machine vision inspection technology has emerged as an indispensable "quality guardian" on production lines, particularly in the label inspection process. It can effectively identify defects such as missing labels, mislabeled labels, and skewed labels.
1. Inspection Principle and System Components
The PET bottle label visual inspection system, based on machine vision technology, performs automated inspection of label quality through image acquisition, processing, and analysis. During operation, a high-resolution CCD camera captures images of PET bottle labels passing through the inspection area from different angles.
The captured images are transmitted to the image processing unit, where they undergo pre-processing and feature extraction before being compared against pre-set standard label templates. When non-compliant defects are detected, the system immediately sends a signal, triggering a rejection mechanism to automatically remove unqualified products from the production line.
A complete visual inspection system typically consists of the following core components:
Inspection Unit: This includes optical components such as a high-resolution CCD camera and LED light source, responsible for capturing label images.
Image Processing Unit: This utilizes specialized image processing software and algorithms to analyze and interpret the captured images.
Human-Machine Interface: This provides an interactive interface, displaying inspection status, fault information, and more.
Control Unit: This is responsible for overall system control and coordination.
Rejection Mechanism: This typically consists of a pneumatic actuator or a sorting robot arm, responsible for rejecting unqualified products.
2. Key Technology Types for Label Inspection
360-Degree Comprehensive Inspection Technology
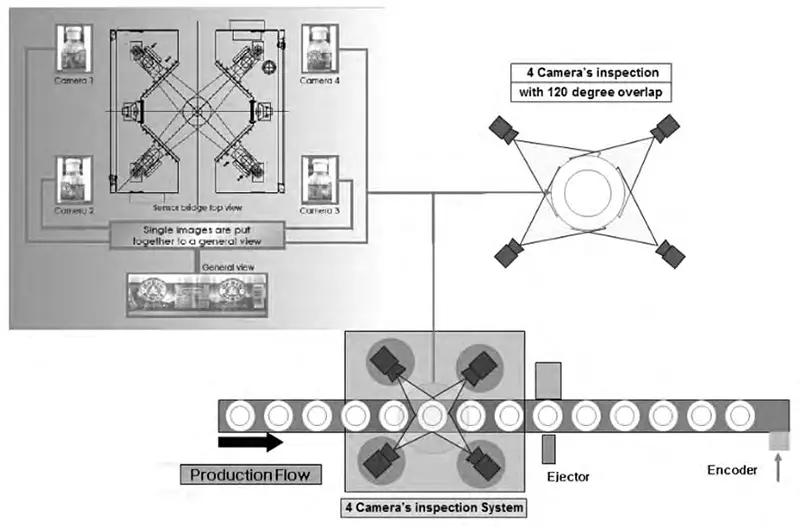
Given the unique characteristics of cylindrical PET bottles, the coordinated operation of multiple cameras is key to achieving comprehensive label inspection. By placing four high-resolution CCD area scan cameras at 90-degree intervals around the product, 360-degree inspection of the label is possible. Another technical approach utilizes a "simultaneous and asynchronous triggering" mode, observing labels from six different angles. Combined with front and backlighting, this method clearly displays the label and its defects. This solution effectively detects defects such as missing labels, labels with joints, labels with high and low profiles, and labels with perforations.
Splicing Inspection Technology
For containers with uncertain rotation angles on the conveyor, the inspection equipment utilizes a soft-light structure and diffuse reflection principles to capture 360-degree images of the label from multiple angles. It then uses a patented stitching inspection algorithm to automatically identify various label defects.
This technology is particularly suitable for inspecting labels on special bottle shapes, such as square bottles, offering advantages such as fast inspection speed and high accuracy.
Optical Imaging Technology
The optical design of the inspection system directly impacts image quality. A telecentric optical configuration effectively reduces image distortion, ensuring accurate and precise inspection. For different label and bottle materials, the system utilizes different illumination methods, such as a combination of front and backlighting, to improve inspection accuracy. 3. Common Label Defects and Detection Capabilities
Visual inspection systems can identify a variety of label defects:
Label presence defects: Basic issues such as missing or missing labels.
Label position defects: Label placement errors such as uneven labels, horizontally offset labels, and tilted labels.
Label integrity defects: Physical damage such as edge cracks, wrinkled labels, warped corners, and perforations.
Label content defects: Content-related issues such as inverted labels, incorrectly cut labels, misprinted labels, and blank labels.
Label type errors: Mismatched labels, mixed labels, and other mismatched labels.
Modern visual inspection systems can achieve inspection speeds of 36,000-48,000 bottles per hour, meeting the demands of high-speed production lines. Using unique image processing algorithms, the system accurately identifies various label defects even when the bottle is slightly rotated.
4. Application Value and Industry Significance
The application of visual inspection technology for PET bottle labels brings multiple benefits to manufacturers:
In terms of quality assurance, automated inspection effectively avoids consumer complaints and market recalls caused by labeling errors. Labels are the primary channel of communication between products and consumers, and their clarity and accuracy directly impact brand image.
To improve production efficiency, visual inspection systems enable continuous, 24/7 operation, significantly reducing downtime and adapting to the demands of large-scale, continuous production. The system's high-speed inspection capacity (up to 48,000 containers per hour) far exceeds the efficiency of manual visual inspection.
From a cost-control perspective, automated inspection reduces labor costs and the reliance on skilled workers. Early detection of labeling issues prevents wasteful packaging materials and reduces subsequent corrective costs.
Visual inspection systems also automatically generate inspection reports, documenting the label status of each bottle and supporting production quality traceability. This feature is crucial for meeting the data integrity requirements of quality management systems such as GMP and HACCP.
5. Implementation Considerations and Future Trends
Successfully implementing a visual inspection system for PET bottle labels requires consideration of multiple factors. Equipment selection should be comprehensively evaluated based on parameters such as line speed, bottle type, and required inspection accuracy.
Installation is typically performed after the labeler/sleeve labeler to detect and reject defective products early in the packaging process. System integration must ensure smooth integration of inspection equipment with other production line equipment, including synchronized control of the rejection mechanism.
In the future, visual inspection technology for PET bottle labels will develop towards a more intelligent and integrated approach:
AI technology application: Integrating machine learning models will improve inspection accuracy in complex scenarios (such as reflective bottles and complex patterns).
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) integration: Linking with MES and ERP systems to achieve intelligent management of the entire production line.
Increasing inspection speed: As production line speeds continue to increase, the processing power of inspection systems will also continue to increase.
Multifunctional integration: Integrating label inspection with cap inspection, liquid level detection, and other functions into a single device to achieve integrated multi-parameter inspection.
With continuous technological advancements, visual inspection systems are becoming increasingly intelligent and efficient. Future inspection equipment will incorporate artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms, enabling them to adapt to diverse production environments and even predict potential quality issues.
For PET packaging manufacturers, investing in advanced visual inspection technology is not only a necessary measure to improve product quality, but also a key component in building an intelligent manufacturing system. Only by integrating modern inspection technology into the entire production process can they remain competitive in an increasingly competitive market.