Application of Machine Vision Inspection Technology in the Beverage Filling Industry
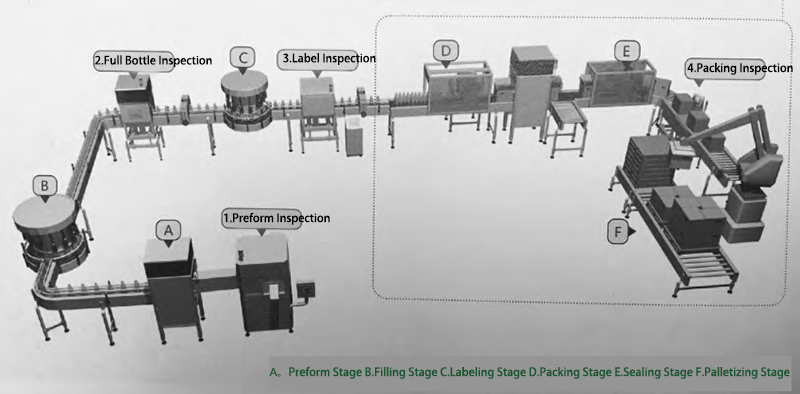
Beverage filling production lines are increasingly moving towards high-speed, fully automated processes. Currently, a typical PET beverage filling line consists of a series of production equipment and corresponding processes, including a blow molding machine, filler, coder, labeler, caser, and palletizer. To maintain overall production efficiency and control finished product quality, advanced machine vision technology is required to automatically identify defects in packaged products and control the corresponding rejection mechanisms to automatically remove damaged and substandard products from the production line. As shown in the following figure: the preform inspection equipment is placed before the blow molding machine to inspect preforms for various defects. The full bottle inspection equipment is placed after the filler to inspect for defects in the capping and coding process. The label inspection equipment is placed after the sleeve/labeler to perform a comprehensive inspection of labels. The case inspection equipment is placed after case packing and before palletizing to check the integrity of the case.
Schematic diagram of the filling line components and the distribution of visual inspection stations
I. Preform Inspection
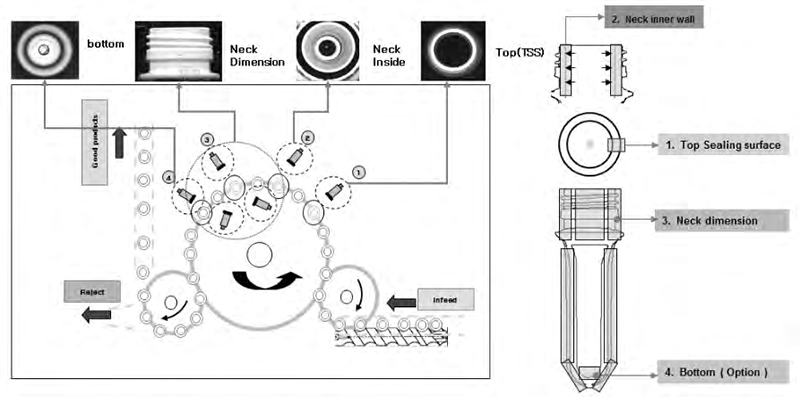
Preform defects are most common in the mouth, shoulder, and bottom of the preform. Preform inspection utilizes six high-resolution CCD cameras to comprehensively inspect the mouth, shoulder, and bottom of the preform for various defects. One camera positioned above the mouth captures images of the mouth surface to detect defects such as burrs, nicks, and black spots on the mouth surface. Another camera positioned above the mouth captures images of the inner wall to detect defects such as black spots and dirt. Three cameras positioned 120 degrees apart on the sides of the threaded mouth provide a 360-degree, no-blinds inspection of the threads and shoulder area for various dimensions, black spots, thick seams, burrs, and steps. A camera positioned above the mouth captures images of the bottom of the preform to detect defects such as black spots and poor sprue.
Preform Inspection Diagram
II. Full Bottle Inspection
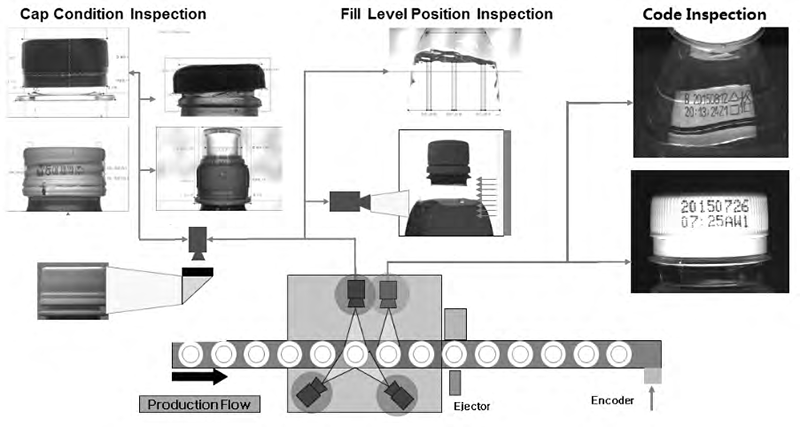
Full bottle inspection can detect defects such as liquid level deviation, broken safety rings, missing PET rings, broken bridges, high caps, crooked caps, mixed caps, missing codes, distorted codes, and partially missing codes. Four sets of high-resolution CCD area scan cameras are deployed. The capping level inspection station consists of three high-resolution CCD area scan cameras, six LED light sources, an image processing system, a signal control system, and a rejection system. The three area scan cameras are positioned 120 degrees apart, providing 360-degree inspection of the caps without blind spots. Each camera is equipped with two LED light sources, illuminating the caps from the front and back. Front illumination primarily detects defects such as broken safety rings, missing PET rings, mismatched caps, and mixed caps, while back illumination focuses on defects such as high caps, skewed caps, and broken bridges. A camera positioned perpendicular to the conveyor belt simultaneously performs liquid level inspection. The combination of front and back illumination effectively compensates for foam, significantly improving liquid level inspection accuracy for beverages containing foam. The coding inspection station uses a high-speed CCD camera and an LED light source for coding inspection. In addition to detecting common coding defects, it can also accurately identify codes to prevent misprints.
Full Bottle Inspection Diagram
III. Label Inspection
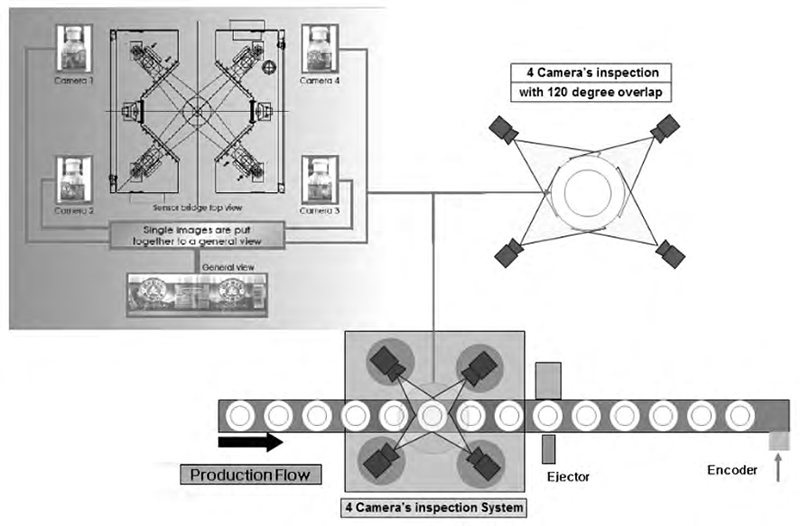
Label inspection can detect numerous label defects, including missing labels, misplaced labels, inverted labels, blank labels, incorrectly cut labels, misaligned labels, tilted labels, misprinted labels, damaged labels, and warped labels. Utilizing a unique optical solution, four high-resolution CCD area scan cameras are positioned 90 degrees apart around the product, providing 360-degree inspection without blind spots. Each camera is equipped with two LED light sources, illuminating the label area from above and below. This combination of top and bottom illumination ensures uniform brightness across the label area, significantly improving the accuracy of label printing defect detection.
Label Inspection Diagram
IV. Case Inspection
Full case inspection is an inline checkweighing system that can be integrated with various packaging production lines and conveyor lines. The inline checkweigher measures the weight of products while they are being conveyed and compares the measured weight to a pre-set value. By checking the weight, the system determines whether any components or products are missing from the package. The control system then performs calculations and issues instructions to remove any unqualified products. The inspection machine consists of a flexible equidistant conveyor, a checkweigher, a rejection system, a control system, and inlet and outlet conveyors. The weighing machine collects product weight signals and transmits them to the control system for processing. The flexible equidistant conveyor increases conveying speed to ensure adequate spacing between products, thus preventing interference between inspection objects. The rejection system, based on instructions from the checkweigher, removes unqualified full cases of product to a temporary storage area for processing. The back-end conveyor transports qualified products after they leave the weighing area.
The widespread adoption of machine vision inspection equipment is imminent, and the Chinese beverage industry will benefit from advances in intelligent equipment technology to achieve the goals of intelligent production and manufacturing.